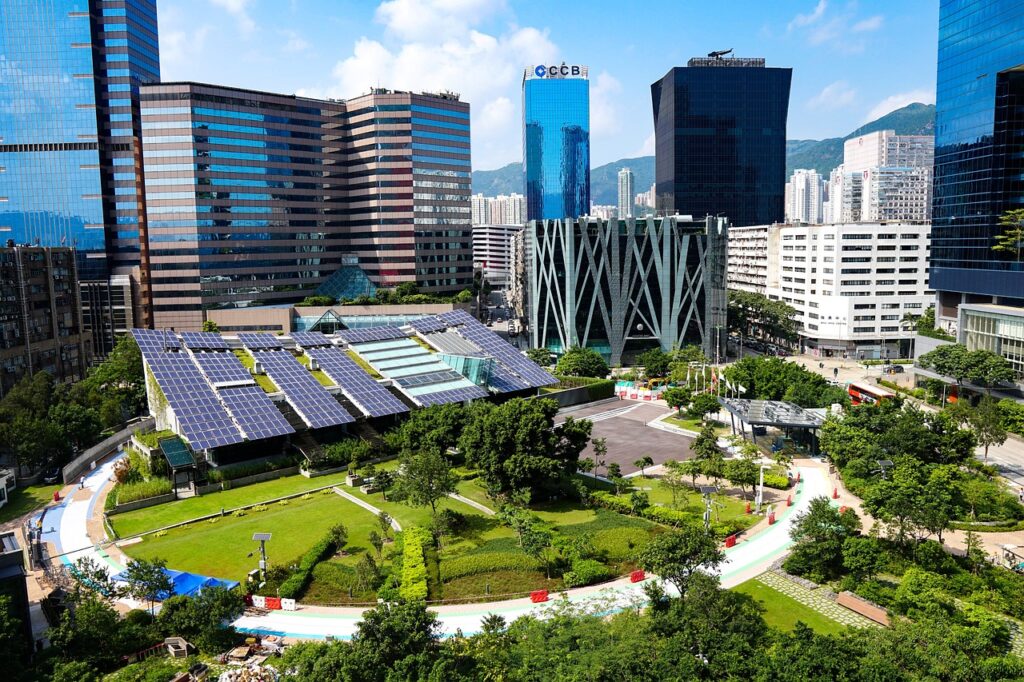
As the world grapples with the realities of climate change and the urgent need for sustainable energy solutions, solar energy technology has emerged as a key player in the renewable energy sector. Solar power harnesses the sun’s energy to generate electricity, offering an environmentally friendly and renewable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. In recent years, there has been a growing interest in incorporating solar energy technology into multifamily developments, as these communities strive to reduce their carbon footprint and promote a sustainable lifestyle for their residents.
By examining the environmental, financial, and social implications of solar-powered communities, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of the potential benefits and drawbacks of embracing solar energy in the multifamily housing sector.
The Benefits:
Environmental Benefits
Solar energy technology produces electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, making it an eco-friendly alternative to traditional fossil fuels. By incorporating solar power into multifamily developments, communities can significantly reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to global efforts to combat climate change. Unlike finite resources like coal, oil, and natural gas, solar energy is a virtually inexhaustible resource. As long as the sun continues to shine, solar power systems can generate clean, renewable electricity. This makes solar energy a highly sustainable option for multifamily developments seeking to promote a green lifestyle.
Financial Advantages
Solar energy systems can help reduce or even eliminate monthly electricity bills for residents in multifamily developments. By generating their own power, these communities can significantly lower their energy costs, resulting in tangible savings for both residents and property managers. Governments often offer tax incentives and rebates to encourage the adoption of renewable energy systems like solar power. However, these incentives and tax advantages vary by state and municipality. Properties with solar energy systems often have higher market values than comparable properties without such systems. As solar power becomes increasingly popular, multifamily developments with solar technology can enjoy a competitive edge in the real estate market, attracting eco-conscious renters.
Energy Independence and Reliability
By generating their own power, multifamily developments with solar energy systems can reduce their reliance on utility companies for electricity. This can provide a measure of energy independence, enabling communities to better control their energy costs and consumption. Solar energy systems, when combined with energy storage solutions, can help multifamily developments maintain power during grid outages or blackouts. This increased resilience can be particularly beneficial during natural disasters or other emergencies, ensuring that residents have access to essential services and resources. Solar energy systems allow multifamily developments to lock in stable energy prices, protecting them from fluctuations in the cost of grid-supplied electricity. By generating their own power, these communities can enjoy more predictable energy costs, making budgeting and financial planning easier for both residents and property managers.
Community and Social Benefits
The installation, maintenance, and operation of solar energy systems in multifamily developments can create local green jobs, contributing to the growth of the renewable energy sector and supporting local economies. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, solar energy systems can help decrease air pollution, leading to improved public health outcomes. Cleaner air can result in fewer respiratory issues, heart problems, and other pollution-related health concerns for residents in multifamily communities. Incorporating solar energy technology sends a strong message about the community’s commitment to environmental sustainability. This can help foster a culture of eco-consciousness among residents and encourage the adoption of other sustainable practices, such as energy conservation, recycling, and water-saving measures.
The Challenges:
Initial Costs and Financial Barriers
One of the primary drawbacks of solar energy technology is the significant upfront cost associated with installing solar panels and related equipment. The average cost per watt to install solar panels in the United States is currently between $1 – $2. For multifamily developments, these costs can be substantial, potentially acting as a deterrent to adopting solar power. While there are financing options available for solar energy projects, some developers and property managers may face challenges in securing funds for their installations. Lenders may be hesitant to provide financing for solar projects due to concerns about their return on investment or the long-term performance of the technology. Although solar energy systems can generate significant long-term savings, the initial investment required may result in a longer payback period. This could make solar energy less appealing to property developers or managers looking for a quicker return on their investment.
Technological and Design Limitations
Multifamily developments may have limited rooftop space available for installing solar panels. This constraint can reduce the potential electricity output of a solar energy system and may require innovative solutions, that add expense, to maximize solar production. There is also the problem with finding space within the property to store the energy being created, which is usually in large Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) batteries. Some property owners, residents, or local planning authorities may have concerns about the visual impact of solar panels on the appearance of multifamily buildings. This can create challenges in integrating solar technology into the design of a development in a way that is both functional and aesthetically pleasing. Solar energy systems depend on sunlight to generate electricity, and their output can be affected by factors such as cloud cover, shade, and seasonal changes. This variability can make it challenging to rely solely on solar power for a multifamily development’s energy needs.
Maintenance and Operational Challenges
Solar panels and other components of a solar energy system require regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure optimal performance. The average cost of a solar panel cleaning is between $400 – $1200, depending on the location and size of the array. Most manufacturers recommend cleaning the panels twice per year. This can create an ongoing responsibility for property managers and additional expense for residents. In multifamily developments, shared solar assets can create complexities in terms of ownership, usage, and cost allocation among residents. Implementing a fair and transparent system for managing these shared resources can be challenging for property managers and may require the development of unique legal frameworks or governance structures.
Conclusion
The adoption of solar energy technology in multifamily developments presents both significant benefits and notable challenges. On the one hand, solar power offers a range of environmental, financial, and social advantages, including reduced greenhouse gas emissions, lower energy bills, increased property values, and a more sustainable lifestyle for residents. On the other hand, there are initial costs, technological & design limitations, and maintenance & operational challenges that must be considered.
By carefully evaluating each project on a case-by-case basis and exploring creative financing options and policy support, multifamily developments can successfully navigate these challenges and reap the benefits of solar energy technology. Ultimately, the integration of solar power into multifamily developments has the potential to contribute significantly to a more sustainable future, playing a vital role in the global transition towards cleaner, renewable energy sources.